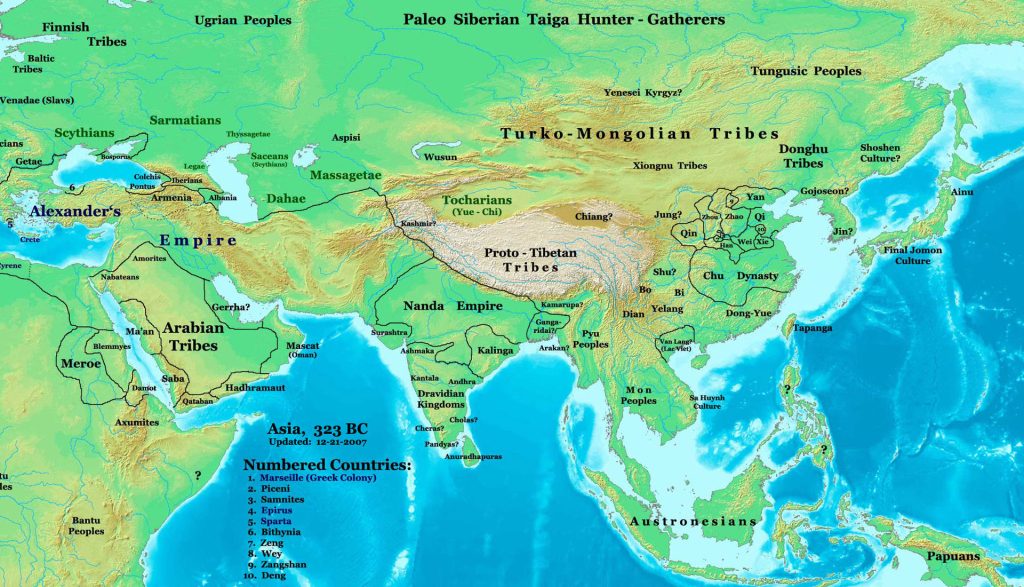
Modern Bangladesh emerged as an independent nation in 1971 after breaking away and achieving independence from Pakistan in the Bangladesh Liberation War. The country’s borders corresponded with the major portion of the ancient and historic region of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, where civilization dates back over four millennia, to the Chalcolithic. The history of the region is closely intertwined with the history of Bengal and the broader history of the Indian subcontinent.
Bangladesh’s early documented history featured successions of Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms and empires, vying for regional dominance.
Islam arrived during the 6th-7th century AD and became dominant gradually since the early 13th century with the advent of Muslim rulers as well as Sunni missionaries such as Shah Jalal in the region. Later, Muslim rulers initiated the preaching of Islam by building mosques. From the 14th century onward, it was ruled by the Bengal Sultanate, founded by king Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, beginning a period of the country’s economic prosperity and military dominance over the regional empires, which was referred by the Europeans to as the richest country to trade with.[1] Afterwards, the region came under the Mughal Empire, as its wealthiest province. Bengal Subah generated almost half of the empire’s GDP and 12% of the world’s GDP,[2][3][4] larger than the entirety of western Europe, ushering in the period of proto-industrialization.[5] The population of the capital city, Dhaka, exceeded a million people.
Following the decline of the Mughal Empire in the early 1700s, Bengal became a semi-independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal, ultimately led by Siraj ud-Daulah. It was later conquered by the British East India Company at the Battle of Plassey in 1757. Bengal directly contributed to the Industrial Revolution in Britain but led to its deindustrialization.
The borders of modern Bangladesh were established with the separation of Bengal and India in August 1947, when the region became East Pakistan as a part of the newly formed State of Pakistan following the Boundary of the Partition of India.[10] However, it was separated from West Pakistan by 1,600 km (994 mi) of Indian territory. The Bangladesh Liberation War (Bengali: মুক্তিযুদ্ধ Muktijuddho), also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh, was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in what was then East Pakistan during the 1971 Bangladesh genocide. It resulted in the independence of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. After independence, the new state endured famine, natural disasters, and widespread poverty, as well as political turmoil and military coups. The restoration of democracy in 1991 has been followed by relative calm and rapid economic progress. Bangladesh is today a major manufacturer in the global textile industry.